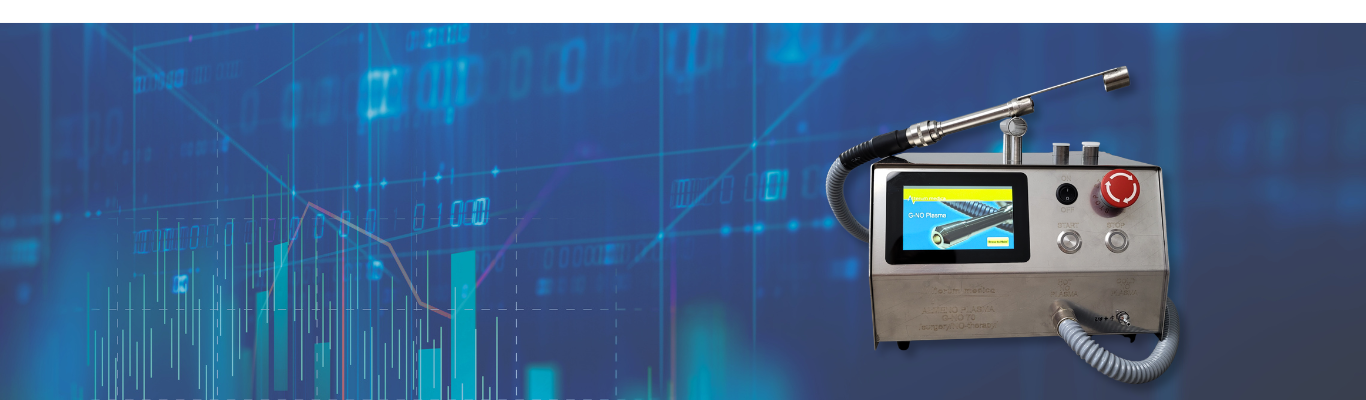

G-NO PLASMA
Method of treatment with Nitric Oxide
NITRIC OXIDE NO IS THE MOST POWERFUL DISINFECTANT
- normalisation of microcirculation (at the expense of vasodilation),
- antiaggregating and anticoagulation effect of NO,
- induction of bacteria phagocytosis by neutrophils and macrophages,
- activation of antioxidant protection,
- increase in secretion of anti-inflammatory pro-recovery cytokines and angiogenesis factors,
- improvement of nerve induction (neurotransmission),
- regulation of specific and non-specific immunity,
- growth of blood vessels,
- scollagen synthesis,
- formation and maturing of granulocytic tissue,
- proliferation of epithelial, apoptosis regulation and prevention of pathological scarring, direct bactericidal effect of NO as well as indirect effect through peroxynitrite,
- formed in tissues during super oxidant interaction
Therapy Procedure
The advantage of the NO-therapy is the ability of exogenous nitric oxide to penetrate not only through the wound surface but also through intact skin and mucous membranes, in other words its non-invasive effect on deep foci and neurovascular bundles.

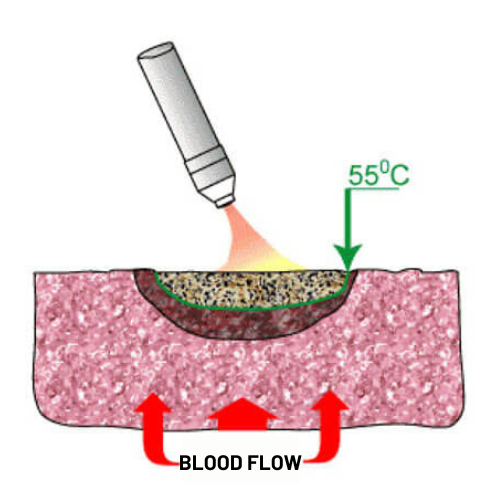
NO acts on biological tissue and heats up. The necrosis layer consists of the degradation product of proteins – partly damaged, unsustainable, but preserving their cellular structure.
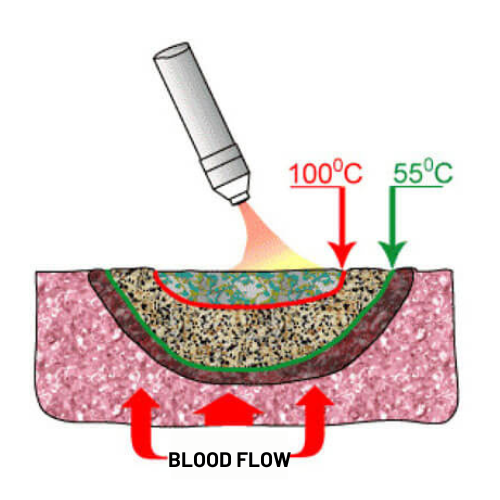
Increasing the exposure time leads to an increase of the boiling process and evaporation of the tissue fluid. A sponge necrosis layer is formed.
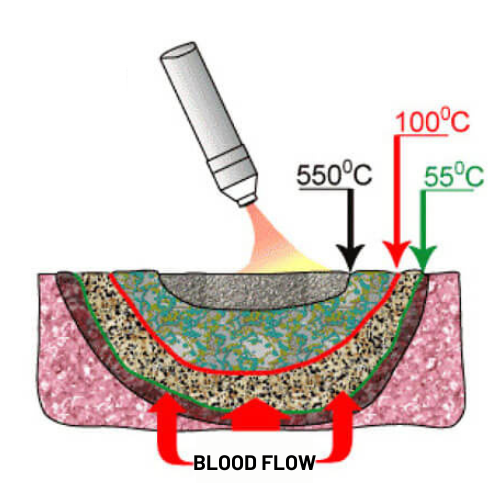
The upper temperature limit indicates that protein and fat breakdown commences in the upper sponge necrosis layer. GOS is carbonized, the necrosis layer is burned, and the tissue is carbonised.
The NO-therapy technology
consists of the exogenous flow of nitric oxide, which normalises the microcirculation of antibacterial effect, activates the antioxidant protection, supresses infection and weakens inflammation and stimulates tissue recovery.
Exogenous diffusion of NO not only through the surface of the wound, but also through intact tissues allows you to act on deep pathological foci, including vascular disorders. Activation of NO increases exogenous NO, which after therapy sharply prolongs the therapeutic effect in the human body.
To learn more, go to:



